R recall
Introduzione all’analisi RNASeq in R
Dipartimento di Biomedicina e Prevenzione
Marco Chiapello, Revelo Datalab
2023-03-31

R variables
Variable
Definition
Variables are used to store information to be referenced and manipulated in a computer program.
They also provide a way of labeling data with a descriptive name, so our programs can be understood more clearly by the reader and ourselves.
It is helpful to think of variables as containers that hold information.
Their sole purpose is to label and store data in memory
Variable
You want your object names to be explicit and not too long.
They cannot start with a number (2x is not valid, but x2 is).
R is case sensitive, so for example, weight_kg is different from Weight_kg.
There are some names that cannot be used because they are the names of fundamental functions in R (e.g., if, else, for, see here for a complete list). In general, even if it’s allowed, it’s best to not use other function names (e.g., c, T, mean, data, df, weights).
It’s best to avoid dots (.) within names. Many function names in R itself have them and dots also have a special meaning (methods) in R.
It is recommended to use nouns for object names and verbs for function names.
Be consistent in the styling of your code, such as where you put spaces, how you name objects, etc.
Variable
Assignment operator
Data Structures
The most essential data structures used in R include:
Vectors: A vector is an ordered collection of basic data types of a given length
Lists: A list is a generic object consisting of an ordered collection of objects. Lists are heterogeneous data structures
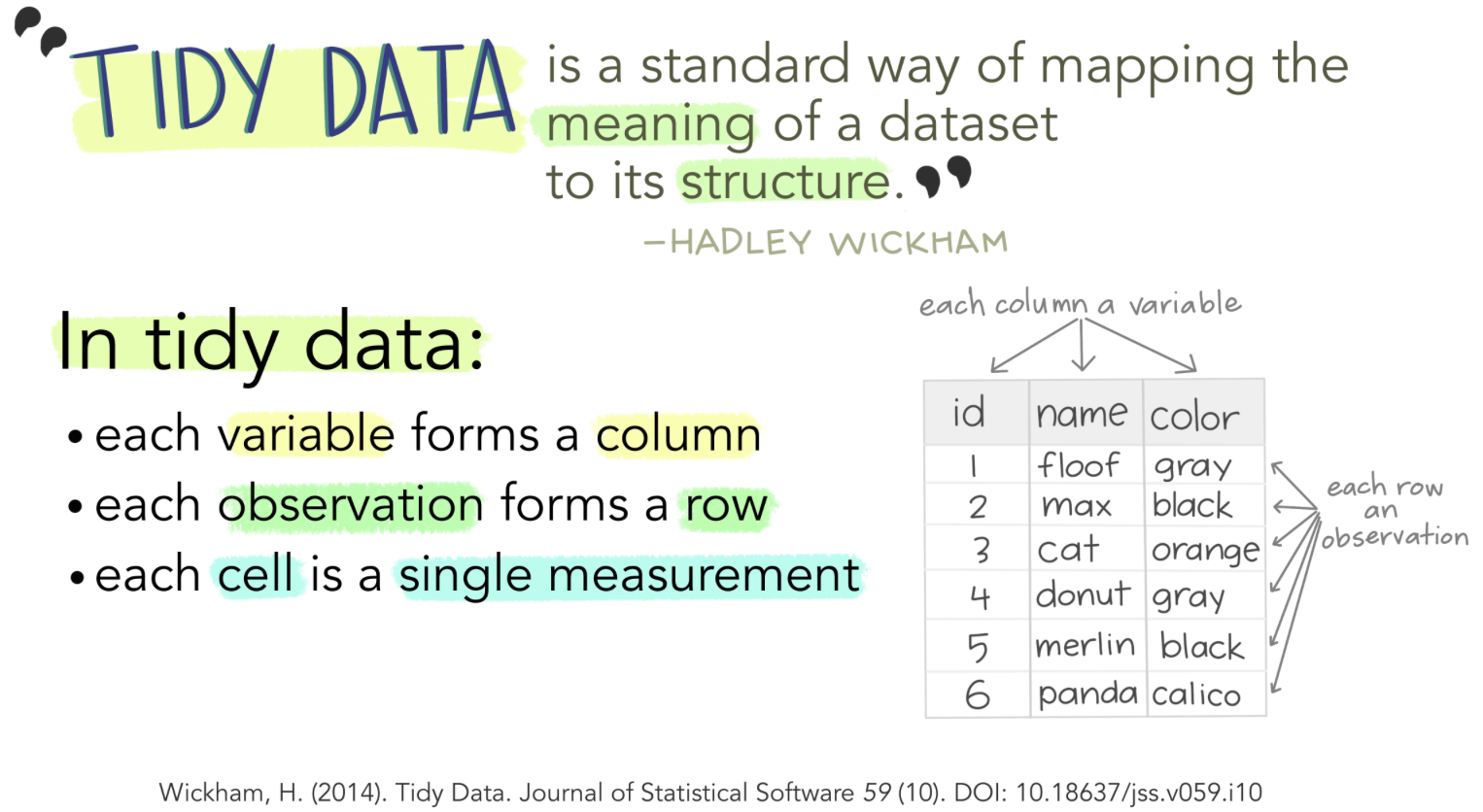
Dataframes: Dataframes are generic data objects of R which are used to store the tabular data. Dataframes are the foremost popular data objects in R
Matrices: A matrix is a rectangular arrangement of numbers in rows and columns. Matrices are two-dimensional, homogeneous data structures.
Arrays: Arrays are the R data objects which store the data in more than two dimensions.
Factors: Factors are the data objects which are used to categorize the data and store it as levels. They are useful for storing categorical data.
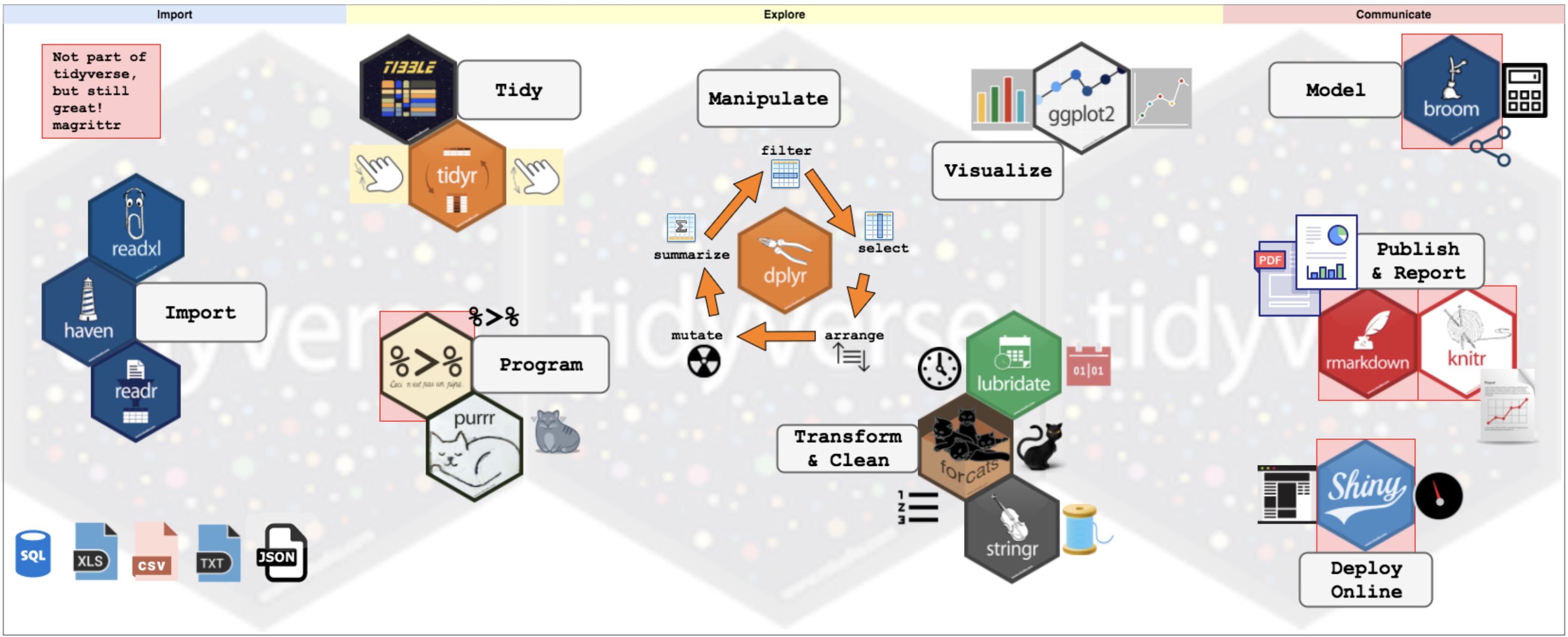
R tidyverse
Bioconductor
Project Goals:
To provide widespread access to a broad range of powerful statistical and graphical methods for the analysis of genomic data.
To facilitate the inclusion of biological metadata in the analysis of genomic data, e.g. literature data from PubMed, annotation data from Entrez genes.
To provide a common software platform that enables the rapid development and deployment of extensible, scalable, and interoperable software.
To further scientific understanding by producing high-quality documentation and reproducible research.
To train researchers on computational and statistical methods for the analysis of biological data.
Domande?
